135.3 Using Git in an IDE and CLI
Compare using Git from within your IDE and from the command line, and learn how to switch between both in a typical development workflow.
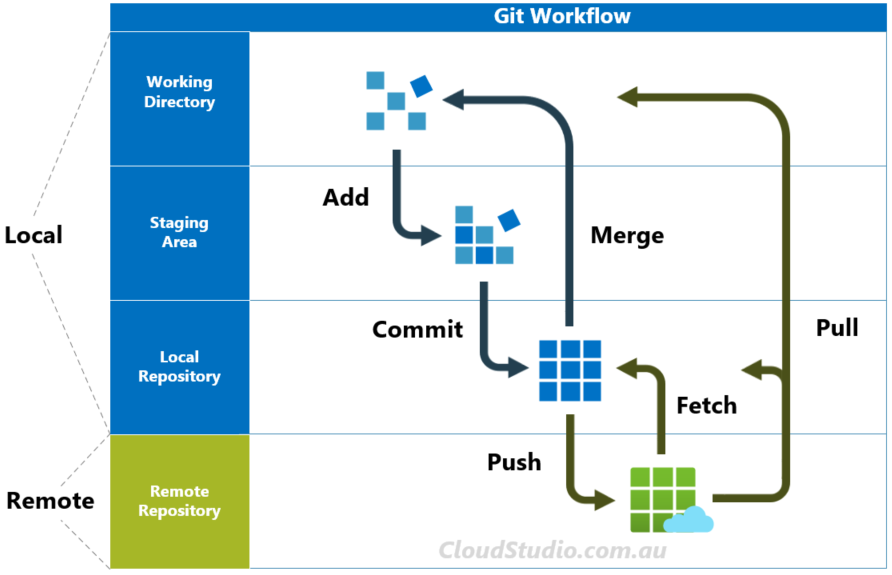
IDE vs CLI: Two ways to use Git
Git in an IDE
Advantages
Example: Git in PyCharm
Git in the command line
Advantages
Common Git commands
Command
Description
Switching between them
Summary
Last updated
Was this helpful?