135.2 Understanding Git and GitHub
Learn the difference between Git and GitHub, how they work together, and how you can use them to manage and share your code.
What is Git?
What is GitHub?
Git vs GitHub: Key differences
Feature
Git
GitHub
Working with both: Local and remote
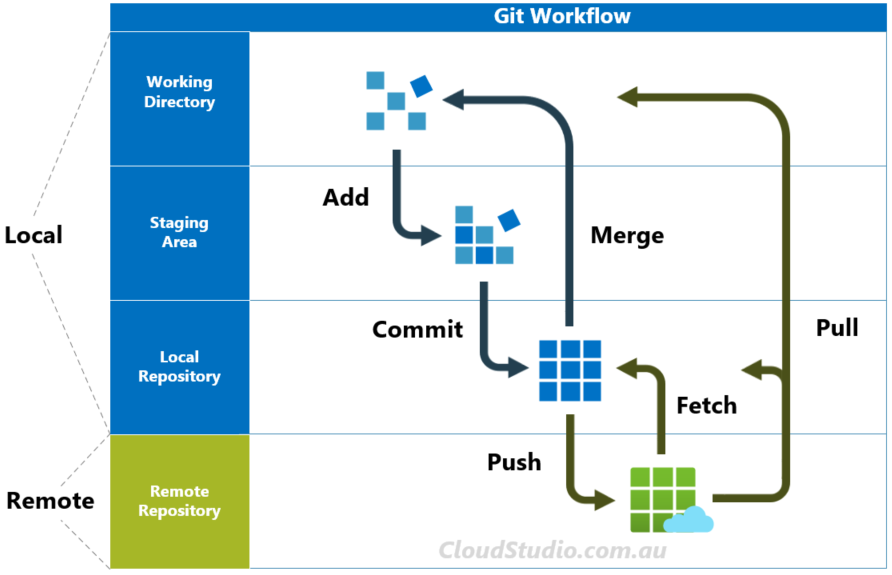
Cloning a project from GitHub
Making changes and pushing them
Summary
Last updated
Was this helpful?